A Relay Electrical Diagram is a crucial tool in electrical engineering, used to illustrate the connection and operation of a relay within a circuit. A relay is an electromechanical switch that enables a low-power electrical circuit to control a high-power circuit. It works by using an electromagnetic coil to open or close contacts that manage the flow of electrical current to a load. This diagram is essential for professionals in electrical control systems, automation, and troubleshooting, as it provides a clear visual representation of how a relay is integrated into a larger electrical circuit.
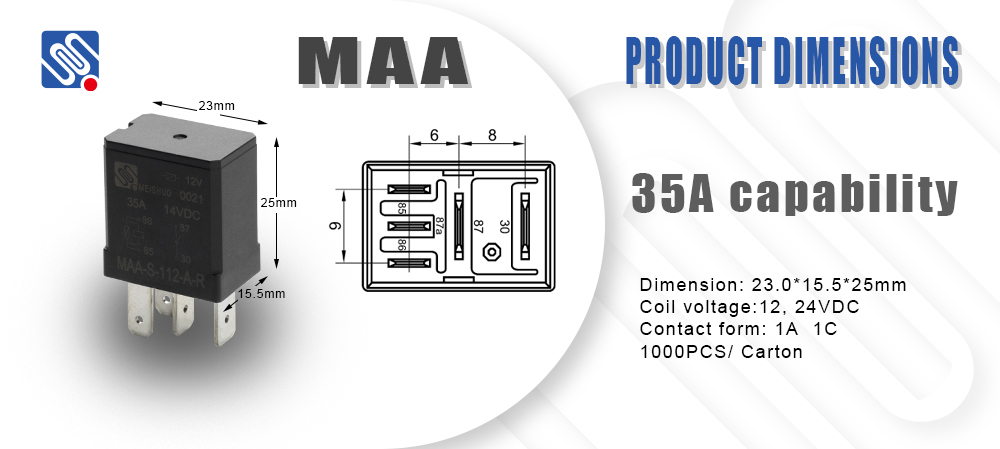
What is a Relay? Before diving into the specifics of a Relay Electrical Diagram, it’s important to understand what a relay is and how it works. A relay consists of an electromagnet (the coil), a movable armature, and one or more contacts. When current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field, causing the armature to move and either open or close the contacts. The relay’s primary function is to control the switching of circuits, usually in response to an electrical signal from a low-power source. Relays come in various forms, including electromagnetic relays, solid-state relays, and time-delay relays. Each type has its specific applications, such as controlling large electrical machines, protecting circuits, or enabling timed operations. Regardless of the type, understanding how these devices interact with a circuit is crucial, and a relay electrical diagram plays a key role in this understanding.