Relay comparison is a technique widely used in various engineering disciplines, particularly in electrical, control, and communication systems. The concept of relay comparison involves comparing input signals or conditions using relays, which are electromagnetic switches that open or close circuits when activated. This article delves into the significance of relay comparison, its applications, and how it plays a vital role in modern technological systems.
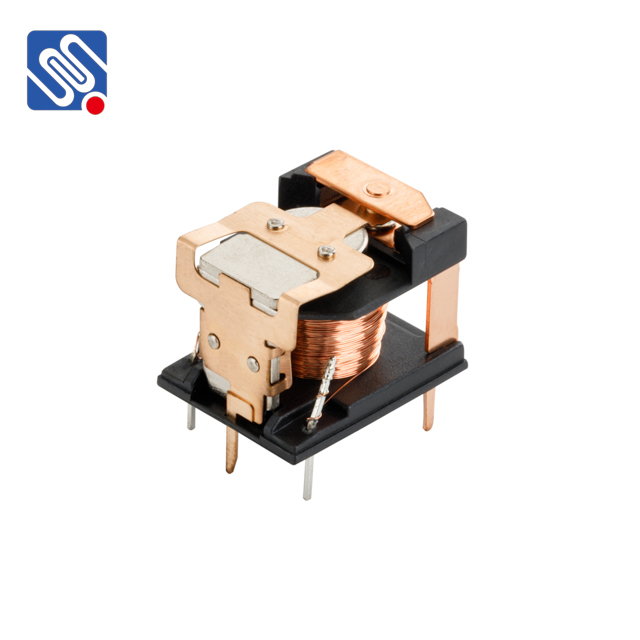
The Role of Relays in Systems A relay is a type of electrical switch that opens or closes a circuit based on an input signal. In its simplest form, a relay consists of a coil of wire that, when energized, creates a magnetic field that moves a set of contacts. These contacts can be used to either complete or break a circuit. Relays are fundamental in many electronic systems because they allow low-power circuits to control high-power circuits. Relay comparison typically involves using two or more relays to compare signals or states in order to make decisions or activate certain actions in response to specific conditions. The use of relay comparison enhances the flexibility and efficiency of a system, particularly when it is important to make automated decisions based on a set of criteria.