A relay electrical diagram is an essential tool in electrical engineering, particularly in the design and analysis of control systems and circuits. Relays are electromagnetic switches that allow for the control of a high-power circuit with a low-power signal. They are commonly used in various applications, from household appliances to complex industrial machinery. This article delves into the structure of relay electrical diagrams, explaining the key components and their functions, along with practical examples of how these diagrams are used in real-world applications.
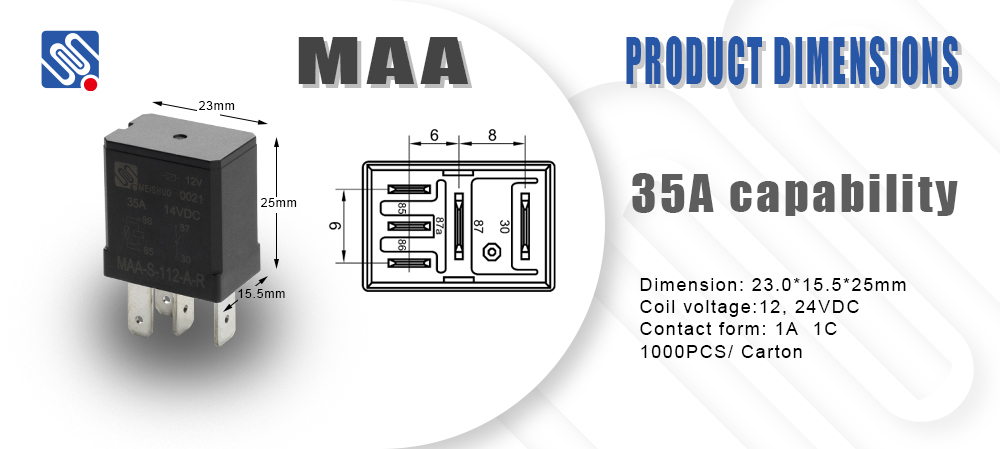
1. What is a Relay? A relay is a device that opens or closes electrical contacts to control a circuit. When an electric current flows through a coil inside the relay, it generates a magnetic field, which either attracts or repels a lever or armature. This action either opens or closes the contacts, thereby completing or interrupting the flow of current in the circuit. In essence, relays function as intermediaries between control circuits and power circuits. 2. Key Components in a Relay Electrical Diagram A typical relay electrical diagram includes several key components, each represented by specific symbols. These components are essential to understanding the relay’s operation and how it interacts with other parts of the electrical system.