Understanding Relay Circuit: Principles, Applications, and Design
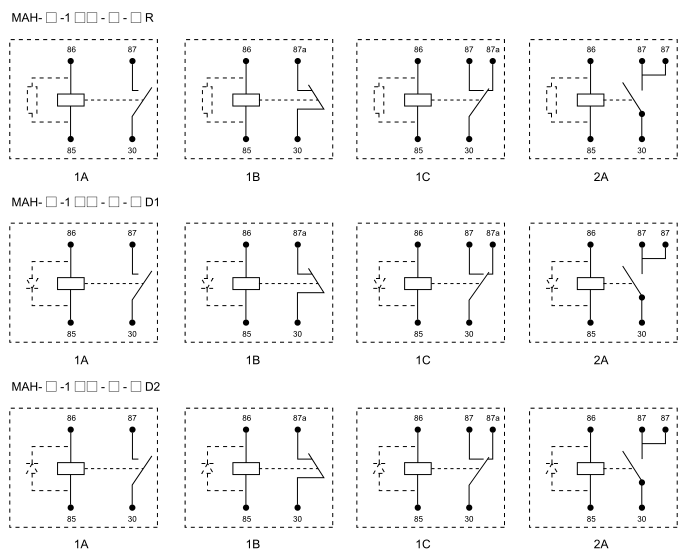
A Relay Circuit is a fundamental component in electrical and electronic systems, widely used for switching purposes. By utilizing an electromagnet, relays allow a low-power signal to control high-power devices, providing isolation between the control and the switched circuit. This article aims to explore the working principle, types, and applications of relay circuits, along with their role in modern technology. Working Principle of a Relay Circuit At its core, a relay operates using the electromagnetic principle. A typical relay consists of an electromagnet, an armature, a spring, and a set of contacts. When an electric current flows through the coil (electromagnet), it generates a magnetic field. This magnetic field causes the armature to move, either closing or opening a set of contacts. These contacts control the flow of current in the circuit, turning a device on or off.